When you want your custom component to accept other blocks, configure your component with children. The following video demonstrates a custom tabs component that accepts Builder blocks as content. Each tab receives a unique block that the user drags and drops in.
To get the most out of this tutorial, you should have the following:
- An app you've integrated with Builder
- Familiarity with using custom components
The most fundamental use case is a basic container that accepts draggable content. This section demonstrates a hero component that users can drag and drop other blocks into.
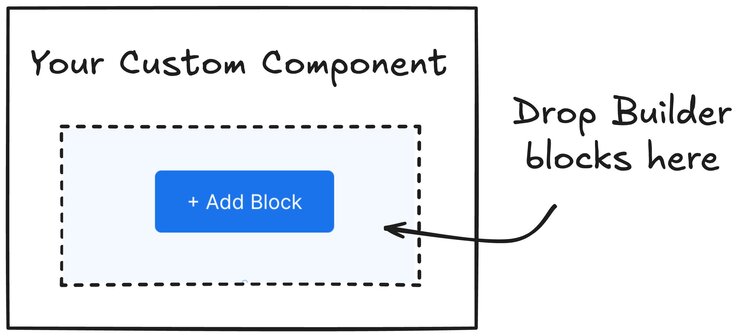
The following video demonstrates adding children to custom components using a basic hero banner.
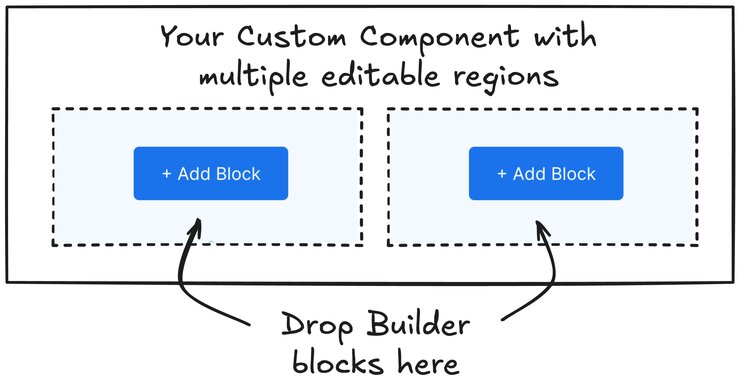
Single editable regions work well for basic components. However, more complex layouts often require multiple distinct areas for content. The next example covers how to create a two-column layout with separate editable regions.
A common need is having multiple distinct areas within a custom component where users can add content. This section covers an example shows how to create a two-column layout where each column is a separate editable region.
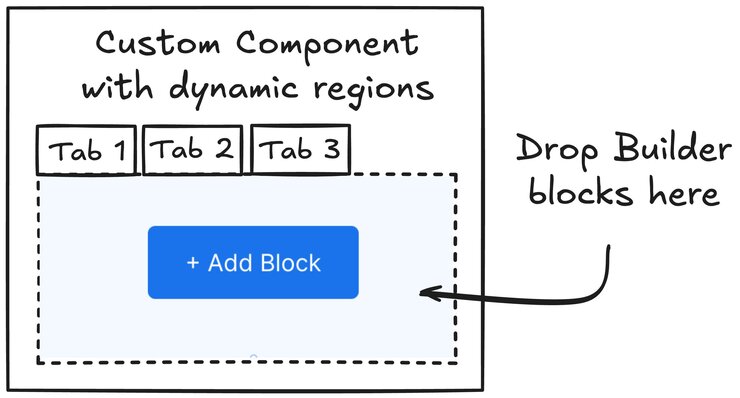
For more complex use cases, you might need multiple editable regions or slots that can be added dynamically. This tabs example demonstrates how to create a component where users can add new tabs, each with its own editable content area.
To customize your components even further, leverage Builder's Input Types.
For more details on child-related options when working with child components, visit the canHaveChildren, childRequirements, and defaultChildren sections of the registerComponent() documentation.
For more examples of custom components with multiple sets of children, visit: